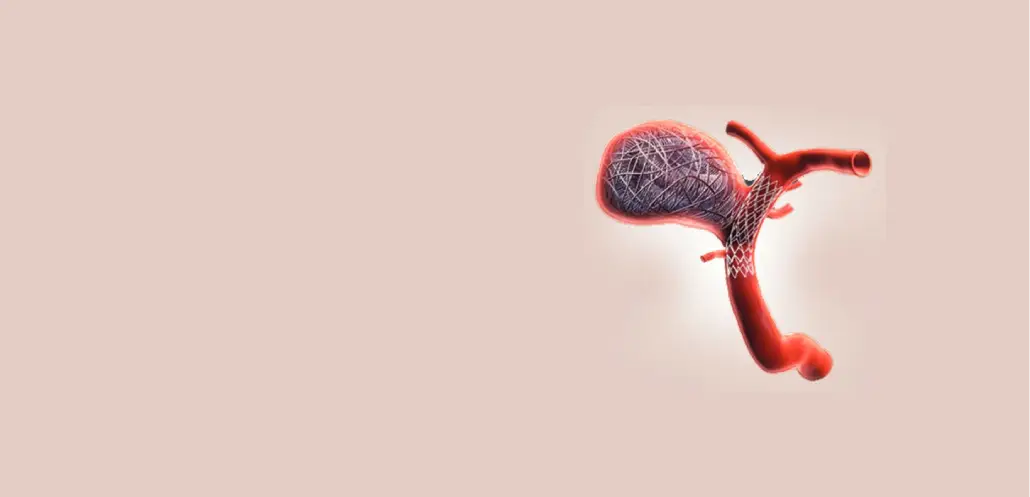
Intracranial aneurysms, often referred to as brain aneurysms, are bulges in the blood vessels of the brain that can pose significant health risks if they rupture. One of the most effective and minimally invasive treatments for certain types of brain aneurysms is a procedure called intracranial aneurysm coiling. This article aims to provide comprehensive education on this procedure, its benefits, and what patients can expect.
What is an Intracranial Aneurysm?
An intracranial aneurysm is a weakened area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain, which causes a localised ballooning or bulge. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to a hemorrhagic stroke, which is a serious medical emergency. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent rupture and ensure the best possible outcome.
What is Intracranial Aneurysm Coiling?
Intracranial aneurysm coiling, also known simply as coiling or endovascular coiling, is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat brain aneurysms. It involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the site of the aneurysm. Tiny platinum coils are then inserted into the aneurysm, inducing blood clot formation and preventing blood from entering the aneurysm, thereby reducing the risk of rupture.
The Procedure
- Preparation: Before the procedure, patients may undergo imaging tests like CT or MRI scans to determine the size and location of the aneurysm.
- Anaesthesia: The procedure is usually performed under general anaesthesia, though in some cases, local anaesthesia may be used.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically in the groin, and guided through the vascular system to the brain.
- Coil Deployment: Using real-time imaging, the surgeon places the coils into the aneurysm. The coils fill the aneurysm, blocking blood flow and promoting clotting.
- Completion: Once the aneurysm is filled with coils, the catheter is removed, and the entry site is sealed.
Benefits of Intracranial Aneurysm Coiling
- Minimally Invasive: Unlike open surgery, coiling does not require a large incision or opening of the skull.
- Reduced Recovery Time: Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and faster overall recovery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: The minimally invasive nature of the procedure generally results in fewer complications compared to traditional surgery.
- High Success Rate: Coiling is highly effective in preventing aneurysm rupture.
- Versatile: Suitable for treating aneurysms in difficult-to-reach locations within the brain.
Commonly asked by Patiemts
-
What are the risks associated with intracranial aneurysm coiling?
While coiling is generally safe, risks can include bleeding, infection, or coil migration. Your interventional radiologist will discuss all potential risks and benefits before the procedure. -
How long does the coiling procedure take?
The procedure typically lasts between 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the aneurysm. -
What is the recovery process like?
Most patients stay in the hospital for a day or two post-procedure. Full recovery can take a few weeks, during which patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities. -
Can all aneurysms be treated with coiling?
Not all aneurysms are suitable for coiling. The decision depends on the aneurysm's size, shape, and location, as well as the patient's overall health. -
How effective is aneurysm coiling in preventing rupture?
Studies show that coiling is highly effective, with a success rate comparable to traditional surgical methods in preventing aneurysm rupture. -
Will I need follow-up after the procedure?
Yes, regular follow-up imaging tests are necessary to ensure the aneurysm remains sealed and to monitor for any changes.
Intracranial aneurysm coiling is a groundbreaking treatment that offers numerous benefits over traditional surgical methods. Its minimally invasive nature, combined with its effectiveness and reduced recovery time, makes it a preferred option for many patients with brain aneurysms. If you or a loved one is facing the prospect of treating an aneurysm, consult with your interventional radiologist to understand if coiling is the right choice for you.
By educating yourself about the procedure, you can make informed decisions and approach your treatment with confidence. Always feel free to ask your healthcare provider any questions you may have, as they are your best resource for information tailored to your specific medical condition.